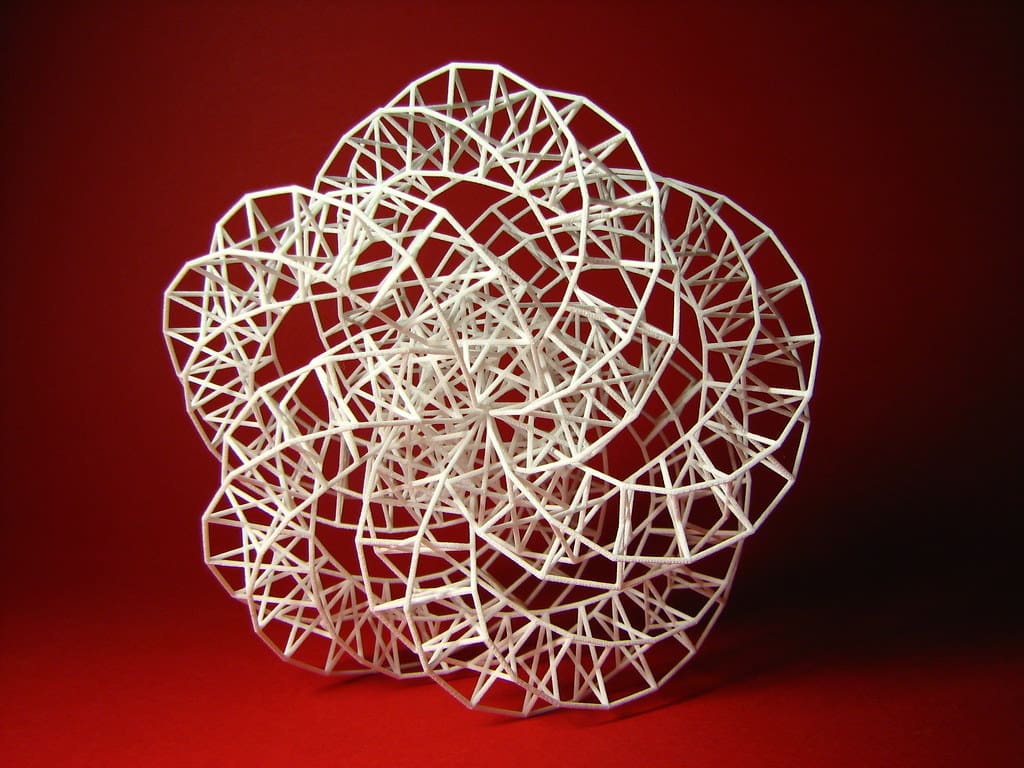
3D printing, a dynamic and evolving technology, has made a significant impact on the art world, providing artists with new realms of possibilities in form, texture, and structure. Known for its precision and versatility, 3D printing enables artists to push beyond traditional boundaries and explore innovative ways of creation and expression. This technology not only transforms how art is made but also expands what can be considered art, marking a new era in artistic innovation.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Art
3D printing introduces several transformative advantages to the art world:
Innovation in Form and Material: Artists can now manipulate materials in unprecedented ways, creating intricate details and structures that were previously impossible. 3D printing allows for complex geometrical patterns and precise repetitions that open up new dimensions in sculpture and installation art.
Interdisciplinary Approaches: The nature of 3D printing encourages the convergence of art with science and technology, fostering collaborations that blend creativity with engineering. This interdisciplinary approach not only broadens the artist’s toolkit but also enriches the conceptual depth of the artwork.
Democratization of Art: 3D printing has democratized the production and distribution of art by enabling artists to replicate their works effortlessly and distribute them globally. This accessibility helps artists reach a wider audience and facilitates greater cultural exchange.
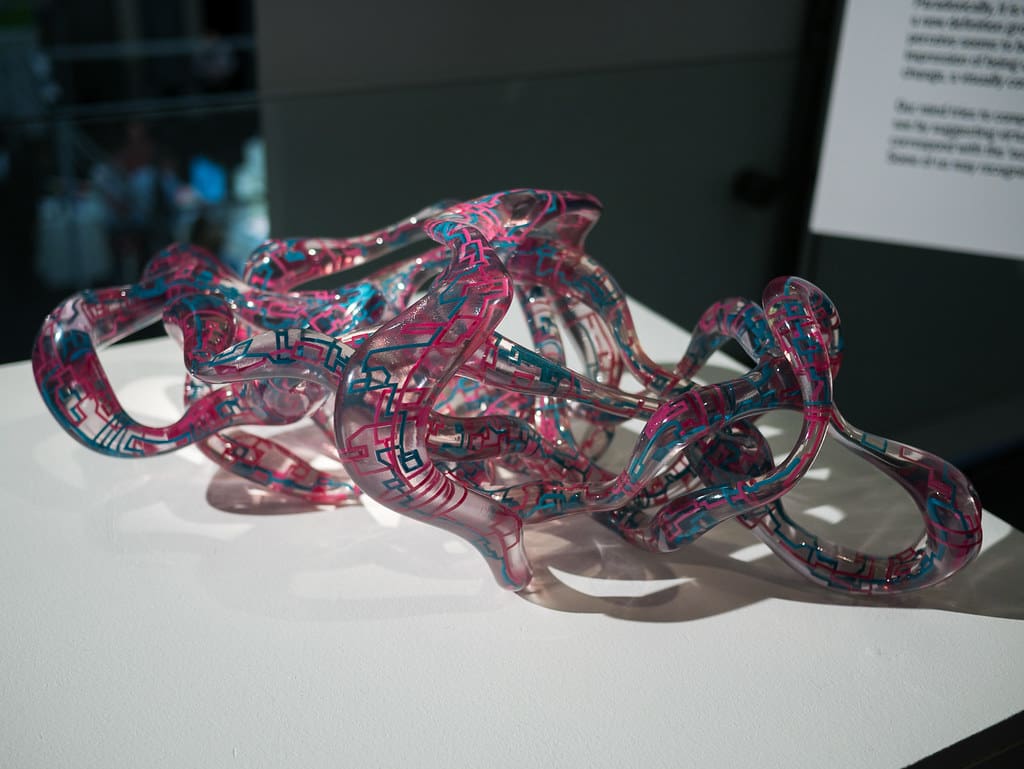

Key Applications of 3D Printing in Art
The use of 3D printing in art spans multiple disciplines and techniques:
Sculpture: Artists like Nick Ervinck and Joshua Harker have utilized 3D printing to create sculptures that defy traditional aesthetics, incorporating fluid forms and intricate details that challenge our perception of space and form.
Installation Art: Installation artists have adopted 3D printing to construct complex, immersive environments that interact with viewers. These installations often feature components that would be too delicate or complex to fabricate by any other means.
Fashion and Jewelry Design: In the realm of fashion, designers such as Iris van Herpen have embraced 3D printing to produce avant-garde collections that merge haute couture with high technology. Similarly, jewelry designers use 3D printing to craft intricate pieces with precision and personalized embellishments.
Performance Art: The integration of 3D printing into performance art has seen artists and designers creating unique costumes and sets that enhance narrative and visual impact. This technology allows for the customization of props and costumes at a level of detail and speed unattainable in the past.
Restoration and Preservation: Museums and conservators use 3D printing to restore and preserve priceless historical artifacts. Replicas can be made for exhibition purposes while the originals are preserved, reducing the risk of damage.
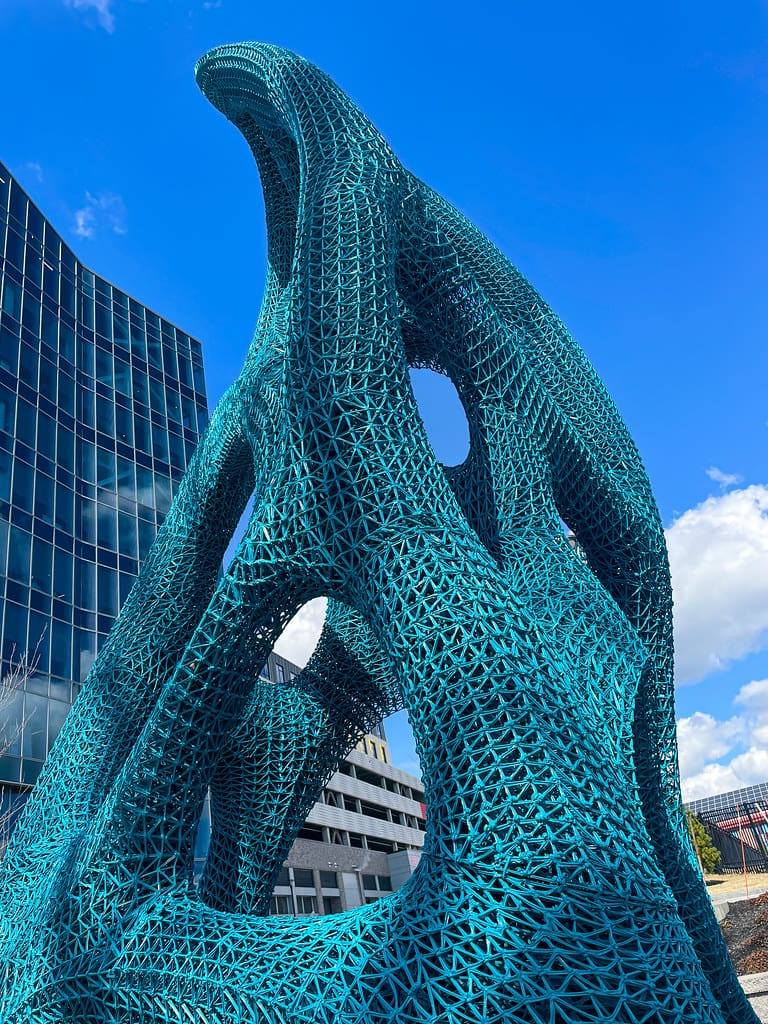

Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, 3D printing in art faces several challenges:
Material Limitations: The range of materials suitable for 3D printing still has limitations in terms of durability and the effect of time, which may influence how artwork ages or is preserved.
Authenticity and Originality: With the ease of replication, questions arise about the authenticity and originality of art pieces. The concept of an ‘original’ becomes blurred when artworks can be reproduced without degradation of quality.
Technological Barriers: There remains a significant learning curve associated with mastering 3D printing technologies. Artists must often collaborate with technologists to realize their visions, which can be both a challenge and an opportunity for creative synergy.
Future Trends in 3D Printing for Art
Looking ahead, several trends suggest exciting developments for 3D printing in the artistic domain:
Material Innovation: Ongoing research into new printable materials promises to offer artists a broader palette, including substances with improved textures, colors, and functional properties.
Cross-Disciplinary Exploration: The future will likely see increased collaboration between artists and scientists, driving forward both aesthetic and technological advances.
Greater Integration in Art Education: As 3D printing becomes more accessible, it is poised to become a standard component of art education, providing students with the skills to merge traditional artistic methods with cutting-edge technology.
3D printing is revolutionizing the art world by opening up new avenues for creativity, expression, and production. As artists continue to explore and push the limits of this technology, 3D printing stands to redefine traditional notions of art in terms of both creation and consumption. For artists and art institutions, embracing this technology not only offers new tools and mediums but also invites a reevaluation of what art can be in the digital age.