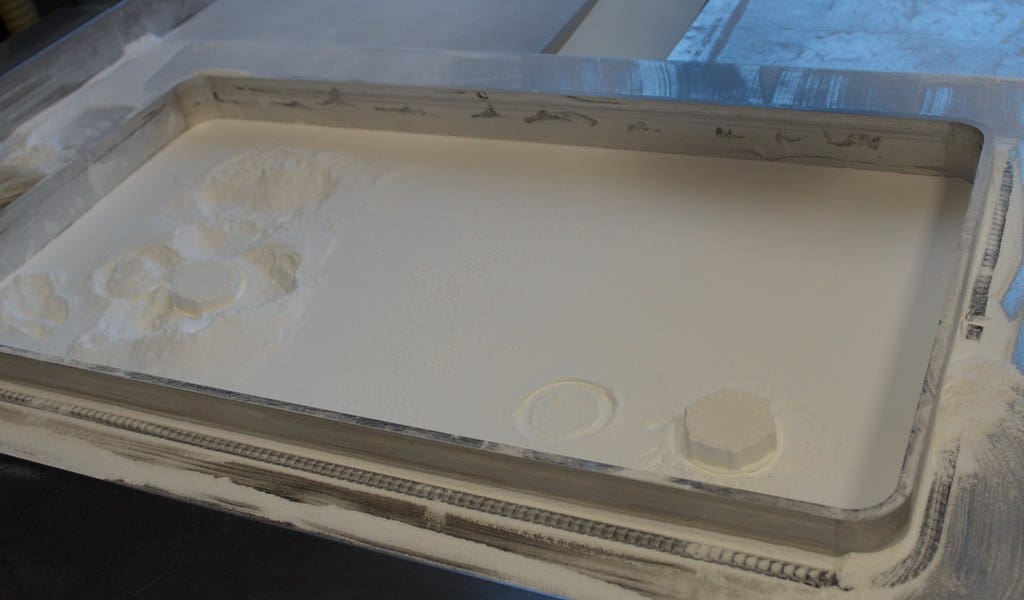
In powder-based 3D printing technologies such as Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), the powder cartridge plays a critical role in material management and operational efficiency. Acting as the primary reservoir and delivery system for the powder used in the printing process, the powder cartridge ensures a continuous, clean, and controlled supply of material to the build area. This article explores the functionality, importance, and maintenance of the powder cartridge in 3D printing, highlighting how it impacts the efficiency and quality of the print.
Importance of the Powder Cartridge in 3D Printing
Material Efficiency: The powder cartridge helps manage the use of expensive and often delicate powder materials by minimizing exposure to the environment and reducing material waste.
Consistent Material Flow: By providing a steady flow of powder to the build platform, the cartridge helps maintain consistent layer thickness and uniform density, which are critical for achieving high-quality prints.
Operational Convenience: Cartridges make it easier to load and unload material, significantly reducing setup and cleaning times between print jobs. This convenience is crucial in high-production environments.
Contamination Prevention: Enclosed cartridges prevent contamination of the powder by environmental factors, ensuring the purity of the material, which is particularly important for achieving the desired mechanical properties in finished parts.
Components of the Powder Cartridge System
Cartridge Housing: Typically made from durable materials that are resistant to wear and chemical degradation, the housing contains and protects the powder.
Feed Mechanism: This includes augers or other conveyance systems designed to move powder from the cartridge to the build area reliably and consistently.
Interface and Seals: Connections between the cartridge and the printer are crucial for preventing leaks and ensuring a clean transfer of powder. These often include specialized seals and locking mechanisms.
Control System: Integrated electronics or mechanical linkages are used to regulate the flow of powder according to the printer’s operational demands.
Installation and Calibration of Powder Cartridges
Proper Installation: Ensuring that the cartridge is correctly installed and securely fastened is crucial to prevent leaks and ensure consistent operation. This may include checking alignment and engaging locking mechanisms properly.
Calibration: Depending on the printer design, calibrating the flow rate and the alignment of the cartridge with the build platform might be necessary to ensure optimal delivery and distribution of powder.
System Integration Testing: Conducting full-system tests after installing or replacing cartridges can help verify that the powder delivery system functions correctly within the broader printer setup.
Maintenance and Optimization of Powder Cartridges
Regular Cleaning: Powder residues and potential clumping should be cleaned from the cartridge and its delivery mechanisms to maintain smooth operation and prevent blockages.
Seal Checks: Regular inspection and replacement of seals and connectors can prevent leaks that might lead to powder loss or contamination.
Powder Management: Managing the type and condition of the powder within the cartridge is critical. This includes ensuring the powder is dry, well-mixed, and free from clumps or foreign particles.
Firmware Updates: For cartridges with integrated control systems, keeping the firmware updated can enhance functionality and compatibility with the printer.
Challenges and Solutions
Material Handling: Different powders may have varying flow characteristics, which can affect their compatibility with standard cartridges. Customizing feed mechanisms or adjusting system settings may be necessary to handle different types of materials effectively.
Wear and Tear: Continuous use can wear down mechanical components like augers or cause clogs in the feed paths. Routine maintenance and part replacements are essential to prevent downtime.
Environmental Sensitivity: Powders can be sensitive to humidity and temperature. Storing cartridges in controlled environments can help preserve material properties and prevent issues like moisture absorption.
The powder cartridge is a vital component in powder-based 3D printing systems, contributing significantly to material efficiency, print quality, and operational convenience. Its role in delivering and managing print material directly affects the printer’s ability to produce consistent and high-quality results. Effective maintenance, proper calibration, and thoughtful integration of powder cartridges into the printing process are crucial for leveraging their full potential and ensuring successful 3D printing operations. By understanding and optimizing the function of the powder cartridge, manufacturers can achieve greater efficiencies and higher-quality outcomes in their 3D printing processes.