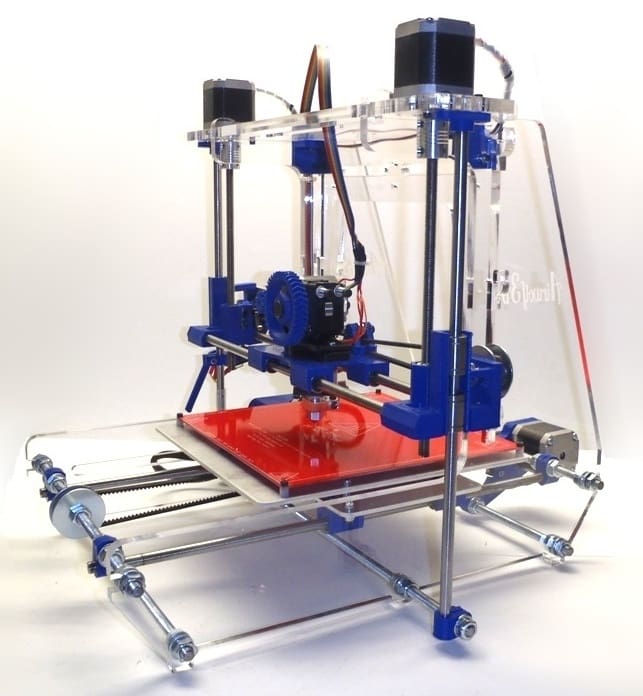
The frame of a 3D printer is not just a physical structure; it is the foundational component that supports and stabilizes the entire printing process. It holds all other components in place and ensures that they operate under optimal conditions to achieve precise and accurate prints. Whether you’re dealing with a consumer-grade desktop printer or an industrial-scale manufacturing machine, the frame’s quality and design significantly impact the printer’s performance and the quality of the final product. This post will delve into the importance, types, materials, and design considerations of 3D printer frames, offering insights into how they contribute to the overall functionality and reliability of 3D printing technology.
Importance of the Frame in 3D Printing
Stability and Precision: The frame’s primary role is to provide a stable and rigid structure that prevents vibrations and movements during printing. Even minor shifts or shakes can lead to flaws in the printed objects, such as layer misalignment or surface inaccuracies. A robust frame ensures that all moving parts, including the print bed and extruder, operate smoothly and consistently.
Support and Integration: A well-designed frame not only supports the physical components of the printer but also facilitates the integration of electrical and mechanical systems. This includes routing for cables, mounting for motors and rails, and spaces for control boards and power supplies.
Heat Management: In printers where high temperatures are used, especially in fused deposition modeling (FDM) and stereolithography (SLA), the frame can play a role in heat dissipation. Metal frames, in particular, can help manage and dissipate heat to maintain a controlled printing environment.
Durability and Longevity: The frame’s durability directly affects the printer’s lifespan. A sturdy frame will withstand wear and tear over many years of use, maintaining its shape and functionality, and protecting sensitive components from external impacts.
Types of 3D Printer Frames
Open Frame: Open-frame designs are common in consumer and educational models. These frames offer easy access to the print area but provide less protection against environmental factors like drafts, which can affect print quality.
Enclosed Frame: Enclosed frames are typical in professional and industrial 3D printers. They provide a controlled environment that minimizes external disruptions. Enclosures can maintain consistent temperature and reduce noise, which is crucial for printing with materials that are sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
Portable Frame: Some newer models feature portable frames designed for easy transport and setup. These are particularly useful for educational purposes, workshops, and demonstrations.
Materials Used in 3D Printer Frames
Aluminum: Aluminum is a popular choice for 3D printer frames due to its excellent balance of strength, weight, and cost. Aluminum profiles, such as those used in T-slot or V-slot designs, are modular and adjustable, allowing for easy customization and assembly.
Steel: Steel frames are exceptionally sturdy and offer greater stability and vibration resistance than aluminum. They are often used in high-end or industrial 3D printers where maximum precision is required.
Acrylic and Wood: Some budget-friendly or DIY 3D printers use acrylic or wood frames. While these materials are less expensive, they can be less stable and durable under the stress of continuous operation.
Composite Materials: Advanced composite materials are sometimes used in specialized 3D printers for their specific properties, such as reduced weight or increased resistance to thermal expansion.
Design Considerations for 3D Printer Frames
Geometry and Size: The design of the frame should accommodate the build volume and ensure there is adequate space for all moving components to operate freely. The geometry should also contribute to the rigidity and stability of the structure.
Assembly and Maintenance: Ease of assembly is an important consideration, especially for kits and home-built models. Frames should be designed to allow for easy access to components for maintenance and upgrades.
Modularity and Upgradability: A modular frame design allows for greater flexibility in modifying or upgrading parts. Users can replace or add components without redesigning the entire system, extending the printer’s functionality and lifespan.
The frame of a 3D printer plays a critical role in determining the printer’s performance, reliability, and longevity. By providing structural stability, it ensures that all other components can function optimally to produce high-quality prints. When choosing or designing a 3D printer, considerable attention should be given to the frame, as it is not merely a supporting structure but a pivotal element that influences every aspect of the printing process. Understanding the types, materials, and design considerations associated with 3D printer frames can lead to better choices and innovations in 3D printing technology, resulting in improved outcomes and enhanced printing experiences.