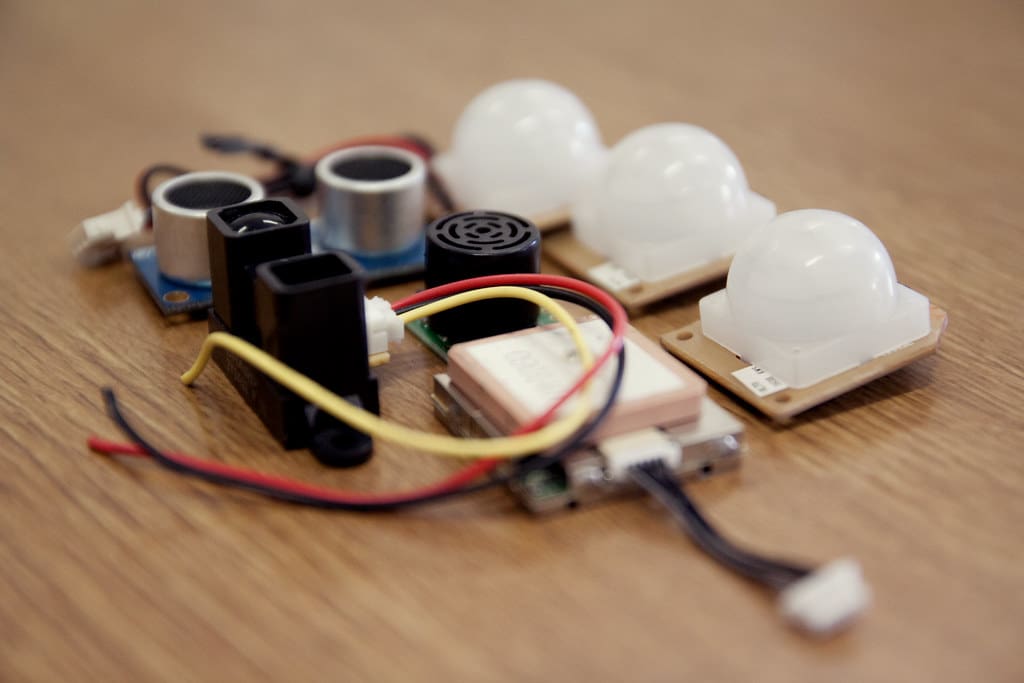
In the intricate world of 3D printing, endstops and sensors play crucial roles in maintaining the precision, functionality, and safety of the printing process. Endstops ensure that the printer’s moving parts do not exceed their intended range, preventing mechanical damage and ensuring accuracy in printing. Sensors monitor various operational parameters, contributing to the overall efficiency and quality of the print. This article explores the different types of endstops and sensors used in 3D printers, their functionalities, and their impact on the printing process.
Importance of Endstops and Sensors in 3D Printing
Precision in Movement: Endstops are used to calibrate the position of the printer’s axes at the start of printing and during operation, ensuring that each print starts from an exact, known position.
Preventing Damage: By defining the limits of the printer’s moving parts, endstops prevent the mechanical components from crashing into each other, which can lead to damage and wear.
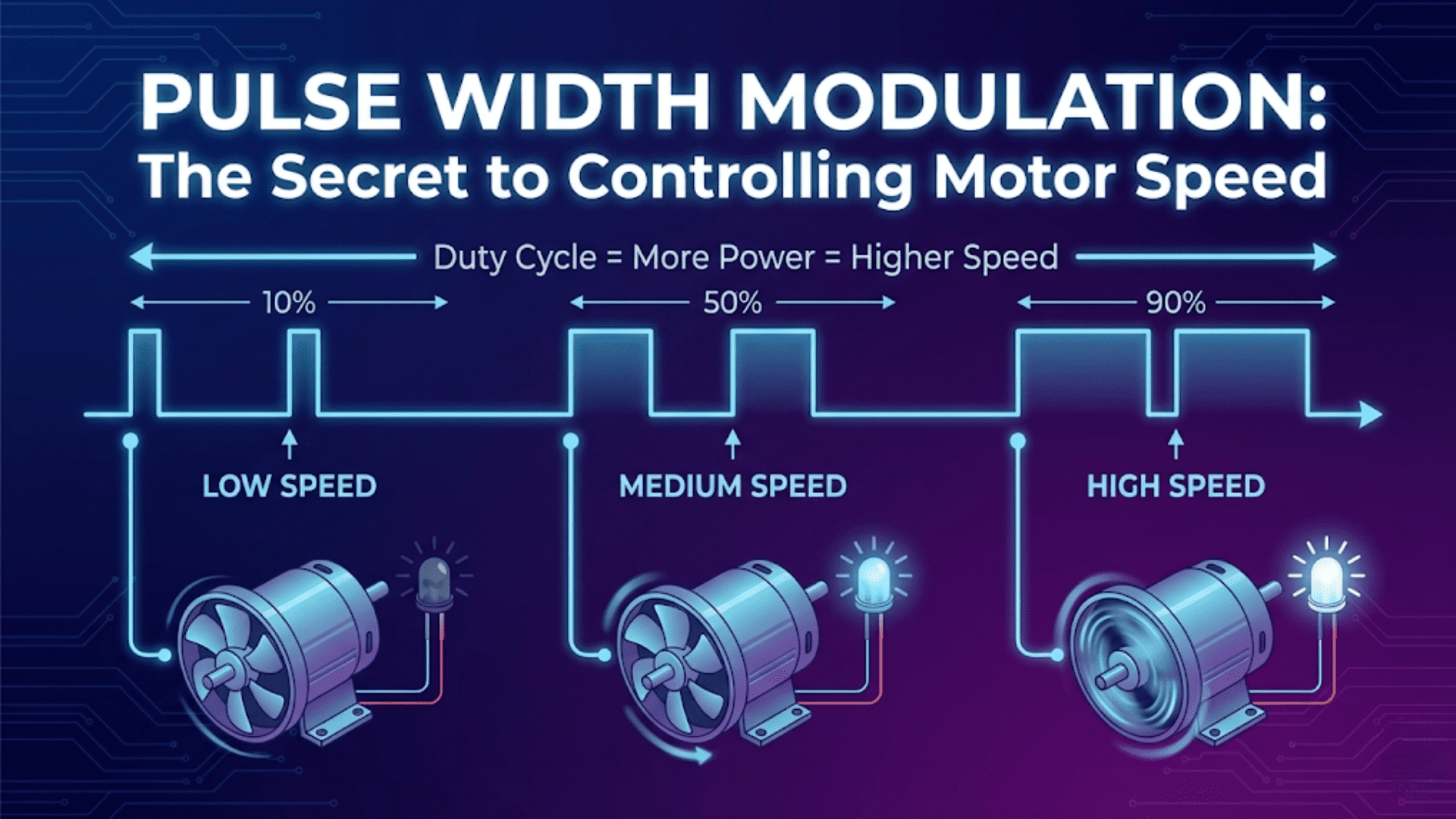
Monitoring and Control: Sensors gather data on various aspects of the printer’s operation, such as temperature, filament presence, and motion, allowing for automated adjustments and improved print quality.
Enhancing Safety: Temperature sensors can detect overheating issues, potentially preventing fire hazards and equipment failure. Filament sensors can pause the printer if the filament runs out, avoiding incomplete prints.
Types of Endstops Used in 3D Printers
Mechanical Endstops: These are the simplest type of endstops, consisting of a switch that is triggered mechanically by the movement of the printer’s parts. They are reliable and cost-effective but can suffer from wear over time.
Optical Endstops: These use a light beam and a sensor to detect when a mechanical part interrupts the beam. Optical endstops are precise and do not suffer from mechanical wear, but they can be sensitive to dust and other obstructions.
Hall Effect Endstops: Utilizing magnetic fields to detect the position, Hall effect sensors are contactless and highly accurate. They are particularly useful in environments where mechanical or optical endstops might fail due to physical contact or dirt accumulation.
Inductive and Capacitive Endstops: Often used for homing in metal print beds, these sensors detect the proximity of metal objects without physical contact. They are durable and precise, making them ideal for industrial-grade printers.
Types of Sensors Used in 3D Printers
Thermistors and Thermocouples: These are used to monitor the temperature of the hotend and the heated bed. Accurate temperature readings are critical for the proper melting and adhesion of filament.
Filament Sensors: These detect the presence of filament and can alert the user or pause the printer if the filament runs out or if there is a jam in the feed system.
Accelerometers: Some high-end 3D printers include accelerometers to detect and adjust for vibrations and other movements that could affect print quality.
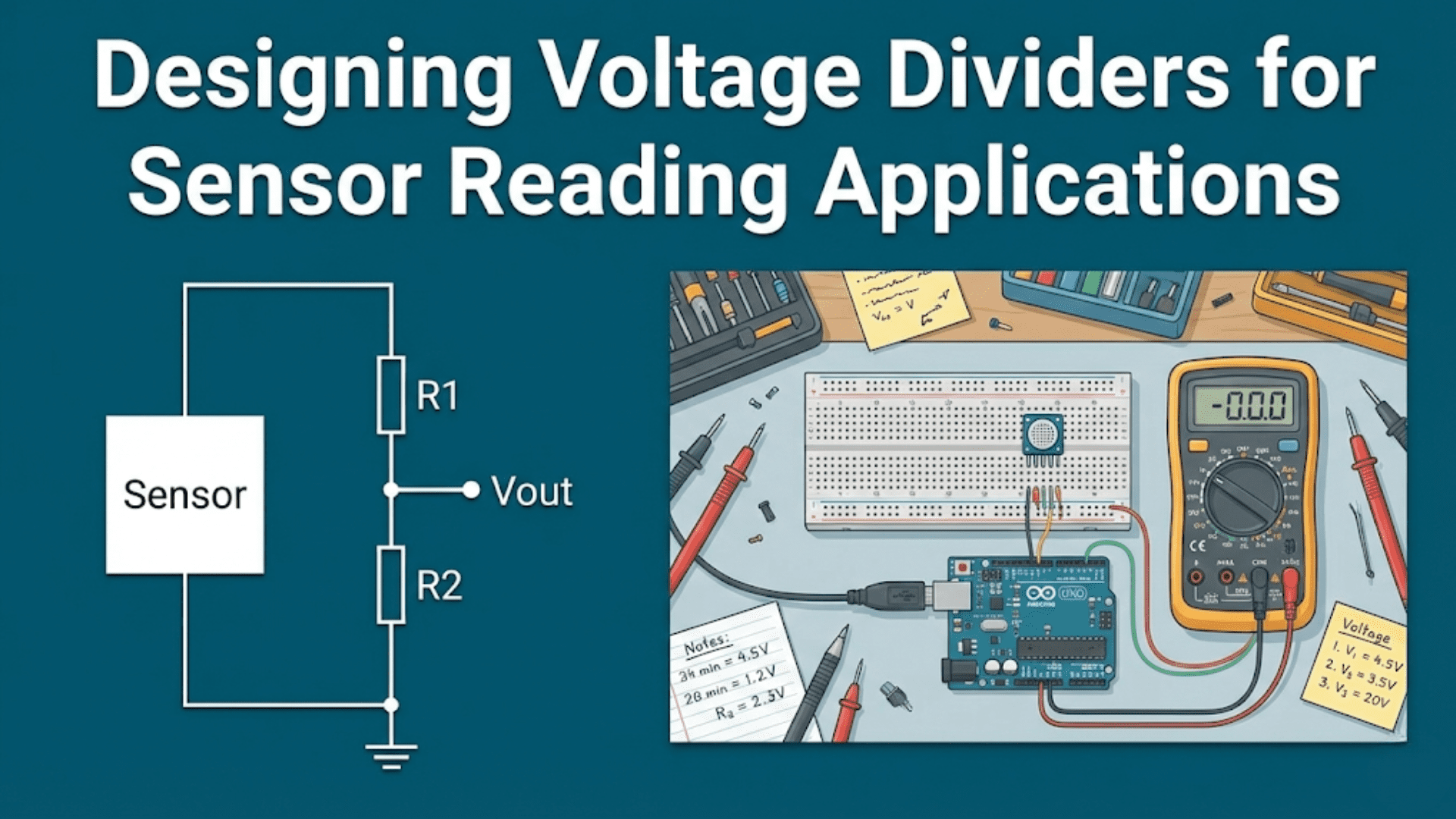
Touch Sensors: Used in automatic bed leveling systems, touch sensors can precisely measure the distance between the print nozzle and the bed surface, adjusting the printer’s g-code in real-time to compensate for any unevenness in the bed.
Installation and Maintenance of Endstops and Sensors
Proper Alignment: Endstops must be correctly aligned with the axes they are meant to control. Incorrect installation can lead to inaccurate homing and reduced print quality.
Regular Calibration: Sensors, particularly those involved in temperature control and bed leveling, require regular calibration to maintain accuracy. This ensures consistent print quality and prevents material waste.
Cleanliness: Optical and some types of contactless endstops are sensitive to dust and debris. Keeping them clean ensures reliable operation.
Firmware Configuration: Proper configuration in the printer’s firmware is essential to ensure that endstops and sensors are recognized and correctly interpreted by the system.
Enhancing Functionality with Advanced Sensors
Upgrades: Upgrading basic mechanical endstops to optical or Hall effect endstops can improve the reliability and precision of the printer.
Integration: Incorporating additional sensors, such as filament sensors or advanced thermal sensors, can significantly enhance the printer’s capabilities, allowing for more complex and reliable printing operations.
Endstops and sensors are foundational components that significantly influence the accuracy, reliability, and safety of 3D printers. They play vital roles in machine calibration, operational monitoring, and preventive safety measures, directly impacting print success and machine longevity. Understanding the various types of endstops and sensors, as well as their proper maintenance and potential upgrades, can help users optimize their 3D printing processes, leading to better quality prints and a more satisfying printing experience.