The build platform in 3D printing, often referred to as the build plate, is crucial for ensuring the successful adhesion and accuracy of the printed models. Whether in a hobbyist’s desktop printer or an industrial-grade machine, the build platform’s design, material, and maintenance play a pivotal role in the overall printing process. This article explores the significance of the build platform, its various types, and how proper care and adjustment can lead to consistently high-quality prints.
Importance of the Build Platform in 3D Printing
First Layer Adhesion: The quality of the first layer is critical in 3D printing, as it sets the foundation for subsequent layers. A well-prepared build platform ensures excellent adhesion, reducing issues like warping and shifting that can lead to print failures.
Heat Distribution: For materials that require heated beds, the build platform’s ability to evenly distribute heat is crucial. This uniform temperature helps to maintain the material’s properties throughout the printing process, ensuring dimensional accuracy and structural integrity.
Surface Finish: The build platform can directly influence the appearance of the bottom layer of the print. A finely tuned and well-maintained platform results in a smoother and more aesthetically pleasing surface finish.
Durability and Reliability: High-quality build platforms can withstand repeated use and exposure to high temperatures and abrasive materials, making them vital for long-term reliability and operational efficiency in 3D printing setups.
Types of Build Platforms
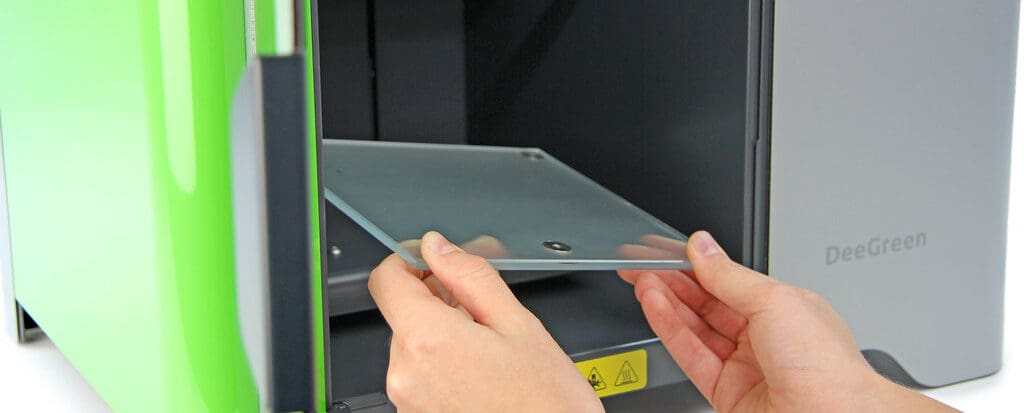
Glass Build Plates: Glass provides a smooth, flat surface that is easy to clean and works well with adhesives and coatings like hairspray or glue sticks. It’s favored for its rigidity and excellent heat distribution, particularly beneficial for materials prone to warping.
Aluminum Build Plates: Aluminum plates are commonly used for their good thermal conductivity, which helps in quickly and evenly heating the build surface. They are durable and work well with magnetic or adhesive flex plates for easy print removal.
Flexible Magnetic Build Plates: These consist of a flexible metal build plate attached to the printer’s bed via magnets. The flexibility allows for easy removal of finished prints by simply bending the plate, making them increasingly popular in consumer-grade printers.
Perforated Build Plates: Often found in printers designed for materials with high contraction rates, such as ABS, perforated plates provide excellent adhesion by allowing the material to grip into the small holes during printing.
PEI Coated Plates: Plates coated with Polyetherimide (PEI) provide a build surface that offers excellent adhesion when heated and allows for easy release of the print once cooled. PEI can be applied as a sheet or directly coated onto another build platform material.
Installation and Maintenance of Build Platforms
Proper Installation: Ensuring that the build platform is correctly installed and leveled is crucial for the success of a print. Most printers offer either manual or automatic bed leveling systems to facilitate this.
Regular Cleaning: Build platforms should be cleaned regularly to remove any residue or debris that could interfere with print adhesion. Depending on the material and type of platform, this could range from wiping with isopropyl alcohol to more intensive scraping and sanding.
Calibration: For printers with heated beds, regular calibration of the heating elements and monitoring of temperature distribution can help in maintaining optimal performance and preventing hotspots or uneven heating.
Surface Treatments: Applying appropriate surface treatments, such as adhesives, release agents, or coatings, can enhance both adhesion during printing and ease of print removal afterward.
Challenges and Solutions
Warping: Warping can occur when the build platform is not properly heated or when the material cools unevenly. Using a heated bed and ensuring proper environmental conditions (such as a closed print chamber) can mitigate this issue.
Adhesion Issues: Prints may not adhere well if the build platform is dirty or if the first layer is not being printed at the correct height. Regular cleaning and recalibration can solve most adhesion problems.
Wear and Tear: Over time, build platforms can become scratched, dented, or otherwise damaged, which can affect print quality. Regular inspections and replacements are recommended to maintain a smooth and reliable build surface.
The build platform is more than just the stage on which 3D printing takes place; it is a critical component that affects the quality, efficiency, and success of the printing process. Understanding the types of build platforms available, along with their proper maintenance and optimization, can significantly enhance the capabilities of any 3D printer. By investing time and care in the build platform, users can ensure consistent, high-quality results across all their 3D printing projects.