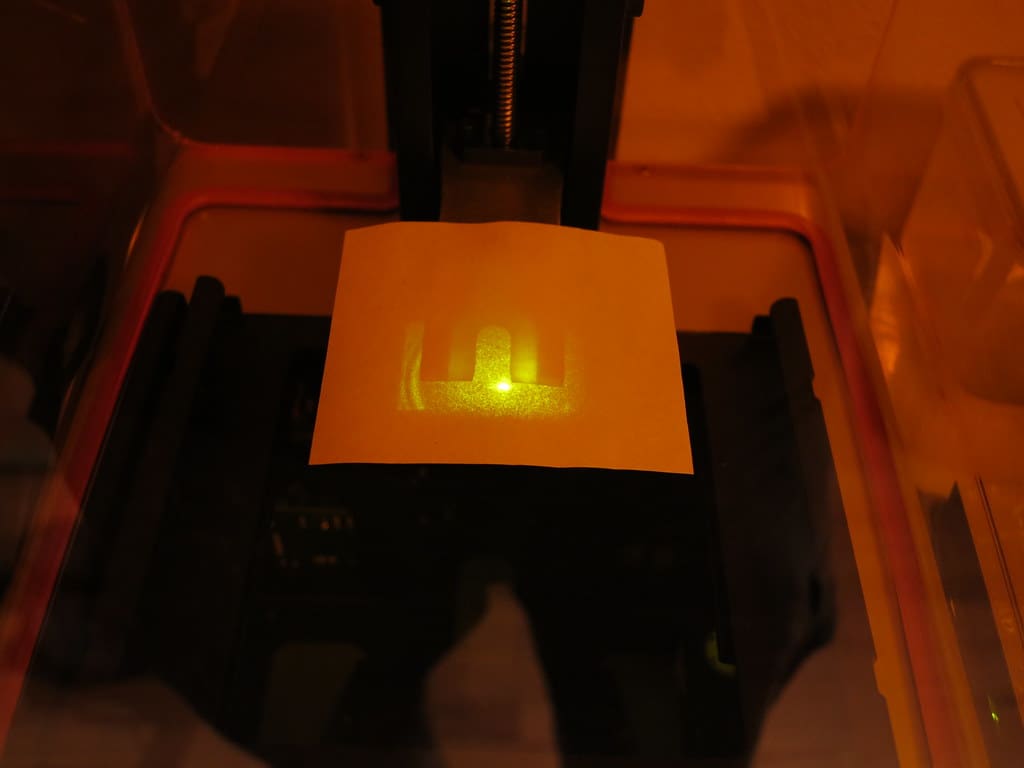
In the field of 3D printing, CO2 lasers play a pivotal role, particularly in laser sintering processes such as Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) for plastics and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) for metals. These lasers are favored for their efficiency, precision, and the ability to work with a wide range of materials. This article delves into the importance, operation, and maintenance of CO2 lasers in 3D printers, highlighting how they contribute significantly to the capabilities and quality of 3D printing technologies.
Importance of CO2 Lasers in 3D Printing
Material Versatility: CO2 lasers can efficiently process various materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics, making them extremely versatile for different 3D printing applications.
Precision and Control: The ability of CO2 lasers to finely control the laser beam’s intensity, duration, and spot size makes them ideal for achieving high precision and detail in the printed objects.
Speed of Operation: CO2 lasers are capable of quickly reaching the required power levels and can maintain consistent energy output, speeding up the sintering process and thereby increasing overall productivity.
Energy Efficiency: Compared to other laser types, CO2 lasers are relatively energy-efficient, which can reduce operating costs and make the 3D printing process more sustainable.
Components of the CO2 Laser System in 3D Printers
Laser Tube: The core component where the laser light is generated, usually filled with a gas mixture including carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium.
Power Supply: Provides the necessary electrical energy to excite the gas mixture in the laser tube, initiating the laser action.
Mirrors and Lenses: Used to direct and focus the laser beam onto the powder bed. These are precisely engineered to handle the specific wavelength of CO2 laser light.
Cooling System: Maintains the laser tube at an optimal temperature to ensure consistent performance and prevent overheating, which could lead to power fluctuations or damage.
Control Electronics: Regulate the operation of the laser, adjusting parameters such as power output, pulse frequency, and beam scanning patterns, based on the design specifications of the 3D object being printed.
Installation and Calibration of CO2 Lasers
Proper Installation: Ensuring that the laser tube and associated optical components are correctly aligned is crucial for optimal performance. Misalignment can lead to inefficient sintering and poor-quality prints.
Calibration: The laser system must be calibrated regularly to maintain accuracy. This includes adjusting the focus of the laser beam and ensuring that the power output matches the requirements for the material being processed.
Safety Measures: Proper enclosures and safety interlocks are necessary to protect operators from laser exposure, as CO2 laser light is powerful and can be hazardous.
Maintenance and Optimization of CO2 Lasers
Regular Cleaning: Optical components like lenses and mirrors must be kept clean from dust and resin debris to prevent scattering and loss of laser power.
Routine Inspections: Regular checks of the laser tube, power supply, and cooling system can help detect issues before they lead to failure or significant downtime.
Component Replacement: Components such as the laser tube and mirrors have a finite lifespan and should be replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommendations or based on performance degradation observed during inspections.
Software Updates: Keeping the laser control software updated can help optimize the performance of the laser system, incorporating new algorithms for improved precision and efficiency.
Challenges and Solutions
Material Interaction: Different materials absorb CO2 laser light at different efficiencies. Testing and adjusting laser parameters for each type of material is essential for achieving the best results.
Thermal Management: Managing the heat input from the laser is crucial, especially to prevent warping or other heat-related issues in the printed parts. Developing effective scanning strategies and using controlled cooling can help manage heat buildup.
Beam Consistency: Over time, the quality of the laser beam may degrade due to wear and tear on the optical components. Regular maintenance and calibration are required to ensure the beam remains consistent and accurately focused.
The CO2 laser is a cornerstone technology in the field of 3D printing, particularly for processes that involve sintering of powdered materials. Its ability to deliver precise, controlled, and efficient energy makes it indispensable for creating high-quality 3D printed objects. Proper management, regular maintenance, and thorough understanding of CO2 laser systems are essential for leveraging their full potential, ensuring that they continue to play a vital role in advancing the capabilities of 3D printing technologies.